Newborn Resuscitation: A way to protect newborn from asphyxia Neonatorum
Definition:
Failure to establish spontaneous respiration immediately after complete delivery of the baby is called asphyxia neonatorum.
- Normal newborn takes first respiration: within 6 seconds, majority within first 20 seconds,
- Rhythmic respiration: by 30 seconds, and majority by 90 seconds after birth
- Normal Rate is 40-60/ min
Prognosis / Consequence asphyxia neonatorum:
- Risk of cerebral palsyAuditory, Visual and language difficulty.
- Intellectually handicapped
Causes of asphyxia neonatorum:
- Failure of respiratory center
- prolonged hypoxia, birth trauma, maternal sedatives within 4 hours before delivery and preterm
- Failure of pulmonary expansion (atelectasis)
- low alveolar surfactant and poor respiratory movements of preterm baby
- Fetal hypoxia causes lung edema
- Obstructed air passageCirculatory collapse in neonatal shock
- Inhaled mcous or meconium and choanal atresia
- blood loss or cardiac abnormality
Signs and syndromes of asphyxia neonatorum:
- Baby does not cry or cries very weakly
- Baby does not breathe or breathes with difficulty, moaning or grunting
- Does not move, extremities limp
- Skin color is blue or pale
- Heart rate is slow or absent
APGAR score:
| Signs | Score 0 | Score 1 | Score 2 |
| Appearance | Blue or pale | Body pink, limbs blue | Pink all over |
| Pulse (heart rate) | Nil | <100/min | >100/min |
| Grimace | Nil | Feeble cry | Cough or sneezing |
| Activity and tone | Limp | Flexion of limbs | Active movements |
| Respiration | Nil | Slow, irregular | Good, crying |
Normal = 8-10. Mild asphyxia = 6-8. Moderate asphyxia = 4-6. Severe asphyxia = 0-3
Immediate Care of the Newborn at Birth (for both normal or abnormal newborn)
- Step-1: Dry and stimuate
- Step-2: Assess breathing and color
- Step-3: Decide if resuscitation is needed
- Step-4: Keep warm
- Step-5: Tie and cut the cord
- Step-6: Start breastfeeding
ABCDS of resuscitation: if needed
• AIRWAY – make sure the airway is open
Position the baby
Suction the mouth and nose ,and if there is meconium, the pharynx (back of throat) also include in suction.
• BREATHING- make sure the baby is breathing
Stimulate to initiate breathing
Use mouth to mouth or ambu bag breathing as necessary
Give oxygen, if available
• CARDIAC FUNCTION- make sure the heart is beating
Stimulate the baby.
Do chest compressions when necessary.
• Dry the mouth
Warm the baby with a blanket, a light, or the mother's skin.
• SHOCK
Make sure the baby is warm and dry.
MANAGEMENT: If resuscitation is needed.
A. Immediate management:
Steps of resuscitation:
- Dry & Wrap
- See Respiration/colour
- Decide for resuscitation
- Position, mouth to mouth respiration, ambu bag
- Cardiac massage
- Intubation
- Drug
Subsequent management:
- Fluid and nutrition should be maintained by IV 10% dextrose, NG tube feeding or oral feeding.
- To control seizure: Inj. Phenobarbitone 20mg/kg IV followed by maintenance dose of 5-6mg/kg per day.
- To control oedema: Fluid restriction 20-25% Mannitol may be used
- IV antibiotic.
Resuscitation Procedure
A. Environment
- Maintenance of temperature
- radiant heater
- warm cloths
B. Positioning
- 1 inch roll of cloth below shoulder


Should not be done always . When?
- Meconium in amniotic fluid
- Asphyxiated baby, first mouth then nose
D) Tactile Stimulation
- Drying
- Flicking of soles
- Rubbing the back
E) Assessment
- Color
- Respiratory effort.
- Heart rate
- Movements or Muscular activities
F) Ventilation
Indications:
- Apnea
- Heart rate < 100 beats
- Persistent central cyanosis
Process:
- Mouth to mouth
- Mouth to mask
- Umbu Bag
- Endotracheal intubation
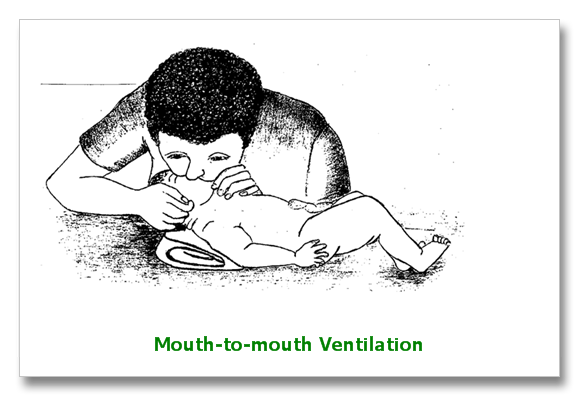
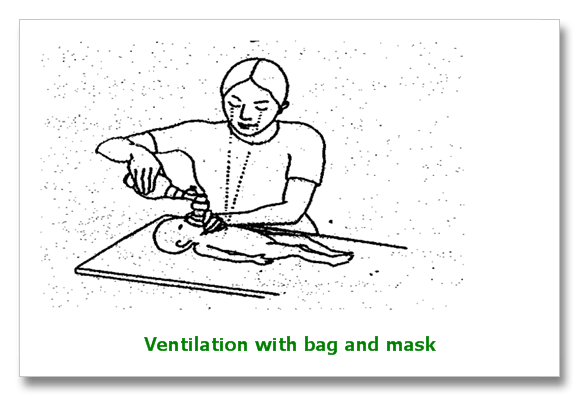
- Rate of 40-60 breaths/min
- Tight face mask should be present
- Initial long inflation pressure-5 in number
- Equal bilateral breath sound should be found
- If good ventilation – count the Heart rate
- If>100 and increase in respiration –stop ventilation
G) Chest compressions
Indications:
- If heart rate is <60 beats/min or 60-80 beats/min and not rapidly increasing despite adequate ventilation with 100% O2 for 30 seconds.
- Discontinuation: Heart rate > 80 b/min

- Heart rate < 80 b/min despite adequate ventilation with O2 and chest compression for 30 sec.
- Route:
- Umbilical vein
- Endotracheal tube
What are the drugs used?
- Adrenaline:
- Dose: 1-3ml/kg of 1:10,000
- Volume Expanders:
- Dose:10ml/kg 5% albumin-Saline or Ringers lactate
- Sodium Bicarbonate:
- Prolonged arrest/or
- profound metabolic acidosis-
- Dose: 2meq/kg of 4.2%
- Naloxone:
- Dose: 0.1mg/kg of 1mg/ml
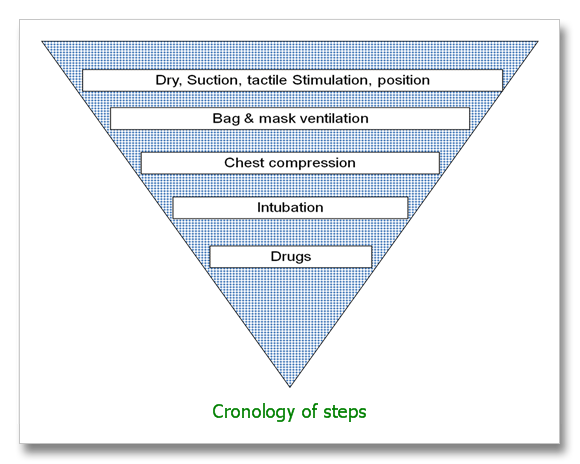
Fig:Inverted pyramid showing relative frequencies of Neonatal resuscitative efforts
If there is no gasping or breathing at all after 20 minutes of ventilation: Stop ventilation
